Narrowband-IoT(NB-IoT)
Introduction
As a network of physical things that use software, sensors, and other technologies for data exchange and connectivity, the Internet of Things (IoT) makes use of the internet to exchange and connect data between systems and devices. From everyday household items to modern industrial equipment, these devices play an important role in our daily lives.
With the increasing demand for IoT devices, there was a need for more efficient and cost effective communication technology. This is where NB-IoT comes in. NB-IoT has been widely used in industries, including agriculture, healthcare, transportation and energy. IoT applications like Smart metering, asset tracking, and Predictive maintenance uses NB-IoT

What is NB-IOT
The “NB-IoT” stands for “Narrow Band Internet of Things”. Taking advantage of low power wide area radio technology, it was published by 3GPP in Release 13 and aims to address the requirements of the Internet of Things (IoT).With the Low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology, indoor and outdoor coverage is improved, low delay sensitivity is achieved, ultra-low device costs are reached, low power consumption is achieved, and an optimized network architecture is implemented.

Unlike traditional cellular networks, NB-IoT focuses on providing reliable and secure communication for devices that require low bandwidth and low power consumption. It is an LTE-based technology that operates in a licensed spectrum making it an ideal solution for IoT applications that require low data rates and long battery life.
Advantages of NB-IOT
After explaining the fundamentals of NB-IoT, let’s take a look at its advantages and disadvantages compared to the other LPWAN technologies.
The reliability of NB-IoT should be mentioned first: because it guarantees the delivery of the data, it gains the upper hand over other LPWAN technologies based on simple access mechanisms. This technology is also highly reliable because it uses licensed spectrum and is not forced to coexist with any other technology.
NB-IoT depends exclusively on the operator, while LoRaWAN can always deploy an extra gateway if coverage is low. The power consumption of a device is also affected by a weaker network coverage: nodes that are covered by weak signals will have to use more power to transmit data, which can result in lower performance in applications that require a minimum battery life (think smart parking
Application of NB-IOT
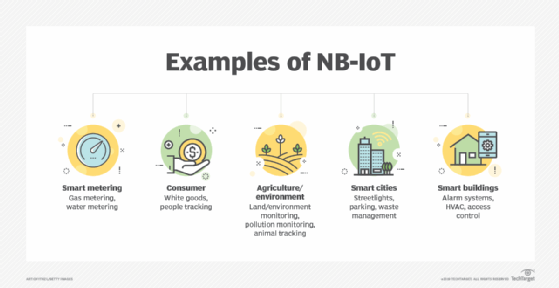
A diversity of networks is often required for IOT applications due to their diversity. For example, key machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, such as remote device operation, works best with LTE or the 5G wireless communications standard. It is sufficient to use LAN or WiFi connections for short-range networks, such as computer networks or home automation devices.
Health Care
Narrowband IoT connectivity opens up possibilities for extensive monitoring and alerting for those who suffer from chronic or age-related diseases, thanks to which doctors will monitor their patients remotely and in real time. Taking the current geosocial situation, solutions are also being developed to help in ensuring the social distancing measures and other pandemic-related policies.
Agriculture and Live stock
As NB-IoT range expands, a wide variety of smart solutions for agriculture and livestock are emerging that aim to achieve a future farm: a set of connected and autonomous agricultural solutions to improve precision and reliability, IoT sensors for measuring condition, livestock tracking (with movement alerts), monitoring soil parameters, pollution rates, intelligent rain prediction, and many more.
Tracking of People or Animals
Wearable devices that support NB-IoT can also be used to track the precise location of their wearers.Designed for elderly people, they are also suitable for pets and animals (pets, cattle…).Even though it may seem disturbing to some, it proves particularly useful when tracking and identifying the movements of infected individuals and their interactions with other individuals or animals.
Manufacturing and Logistics
With the right technology, it will be much simpler to adopt smart factory solutions like geolocating moving assets to optimize logistics, checking their status, and gathering important data about them. Additionally, NB-IoT-based solutions will make it possible to follow, monitor, and diagnose production objects in real time so that a failure can be prevented (predictive maintenance).
Smart Homes and Buildings
Using NB-IoT to manage emergency or anti-theft alarms in residences and commercial buildings, smart consumption measurements (for electricity, gas, and water), intelligent lighting and air conditioning, and air quality monitoring could result in lower costs and a smaller environmental effect.
Smart Cities
Local governments will be able to effectively manage street lighting, open parking spots, the environment, and a lot more thanks to the opportunities provided by NB-IoT.
NB-IOT and Other Low power Wide area networks(LPWANs)
Low power wide area networks or LPWANs. As a generic term, it refers to any network of connected devices that uses less power than other communication technologies, such as telephones, satellites, and wireless networks.
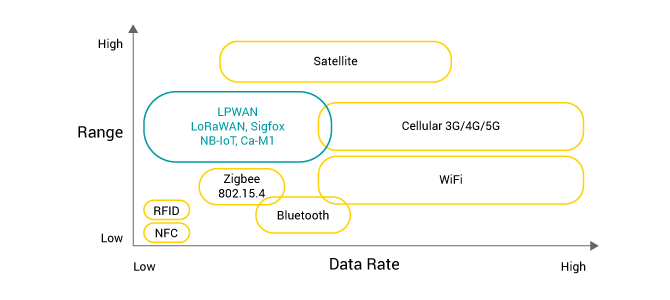
As with the LTE Advanced and 5G standards, modern telephone networks can transmit data at speeds of several gigabits per second; however, LPWA offers significantly slower speeds, often only a few kilobits per channel. As a result, many IoT protocols such as LwM2M and others are able to grow rapidly because they manage technology that is resource-constrained (such as IoT sensors, actuators, and controllers).
Cellular v/s Noncellular LPWANs
In the LPWA ecosystem, there are two main technologies: one relies on cellular connectivity, while the other was developed as a non-cellular alternative to the GPRS standard that was popular in the past.
Non-cellular network solutions

To reduce energy consumption and costs of connected devices, Sigfox has been developed to work independently of traditional telecommunication infrastructure. Apart from being low-speed, the communication is also based on a narrow band, which allows the devices to penetrate obstacles better, facilitating communication even over long distances, even in urban areas. As part of the Sigfox network, antennas and base stations are distributed across the territory that collect and transport data from endpoints to the Sigfox server.

The LoRa protocol is a non-cellular modulation technology for implementing LoRaWAN. However, these two terms – LoRa and LoRaWAN – are not interchangeable: while LoRaWAN is the standard protocol for WAN communications, LoRa should be understood as a wide area network technology.
Cellular network solutions

LTE-M is a network technology standard based on 4G published by 3GPP in version 13 of its specifications. In order to meet the criterion of low power stipulated in the LPWA specification, the 4G wireless chips have been designed based on a special power-saving mode. In essence, the chips are off most of the time, and only wake up at predetermined intervals. In addition, the chips are semi-duplex, so they use less power even when they are turned on.
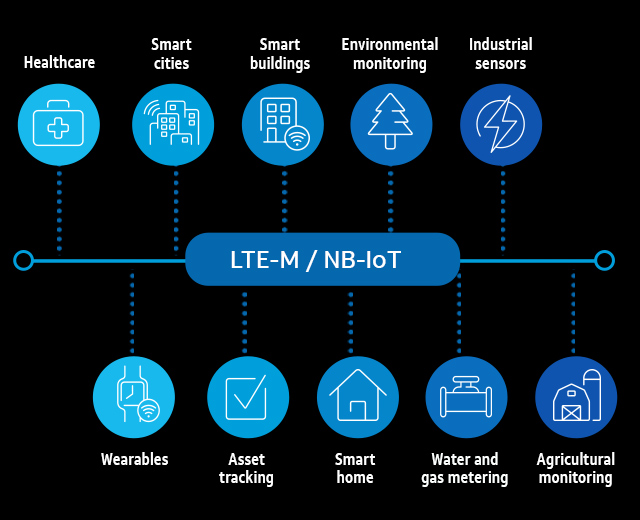
Conclusion
In conclusion NB-IoT technology is a cost effective, low-power and highly secure communication technology that has been specifically designed for IoT application. Considering its robustness, scalability, and efficiency, we will likely see more applications using it in the future.


